The glut of Ancient Egypt's giant-sized temples and tombs lined with vibrant wall paintings you can visit here makes the town an open-air museum, while if there are only so many monuments you can cope with, there are hot-air ballooning and felucca rides to temper temple overload.
This was the site of ancient Thebes, the great city of the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom pharaohs, who covered the banks of the Nile with their mammoth building works and began the vast tomb structures snugly hidden amid the rocky valley of the West Bank.
The scope of their ambition is best appreciated today in the magnificent Karnak Temple complex, but there are so many monuments here that you could easily spend a week simply soaking up Ancient Egypt's ambition and grandeur.
This is the best place to visit in Egypt to simply lose yourself in the wonders of the ancient world.
With so much to see and do, plan your trip with our list of the top attractions in Luxor and easy day trip ideas from the city.
1. Temple of Karnak
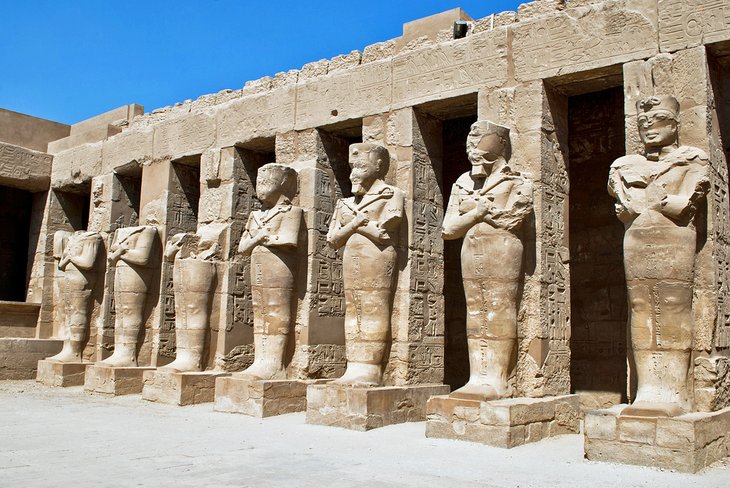

Of Luxor's many monuments, the Temple Complex of Karnak has to be its most astonishing and beautiful feat.
Within its precincts are the Great Temple of Amun, the Temple of Khons, and the Festival Temple of Tuthmosis III, as well as surrounding minor temples and sanctuaries.
The complex is not built to a single unified plan. Instead, it represents the building activity of many successive rulers, who vied with one another in adding to and adorning this great national sanctuary, which became the most important of Egypt's temples during the New Kingdom.
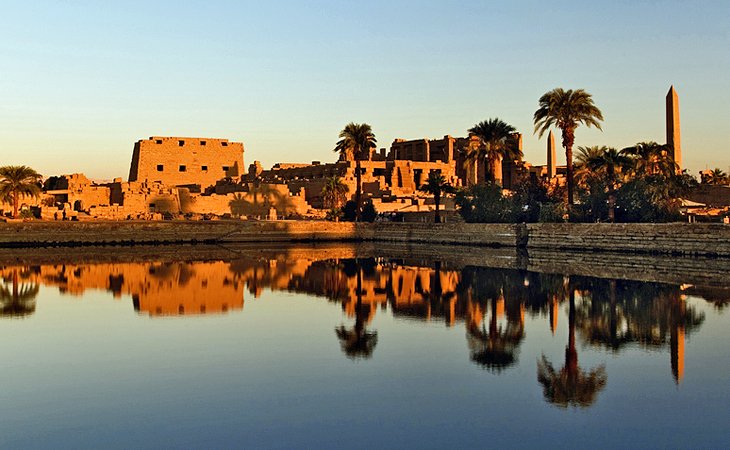

All the monuments here are built on a gigantic scale, reducing visitors to ant-like proportions as they gaze up at mighty columns and colossal statuary.
Even if you're short on time, don't scrimp on your visit here. You need at least three hours to try and make sense of the entire complex.
You can easily walk to Karnak from downtown along the Nile-side Corniche road, although due to the heat most people take a taxi.
If you're short on time, plenty of tours are offered that whip you around the highlights of Karnak. A private tour of Luxor East Bank, Karnak, and the Luxor temples is a good option. This half-day tour visits these ancient sites with an Egyptologist.
Address: Maabad al-Karnak Street, East Bank, Luxor
- Read More: Exploring The Temples of Karnak: A Visitor's Guide
2. Valley of the Kings
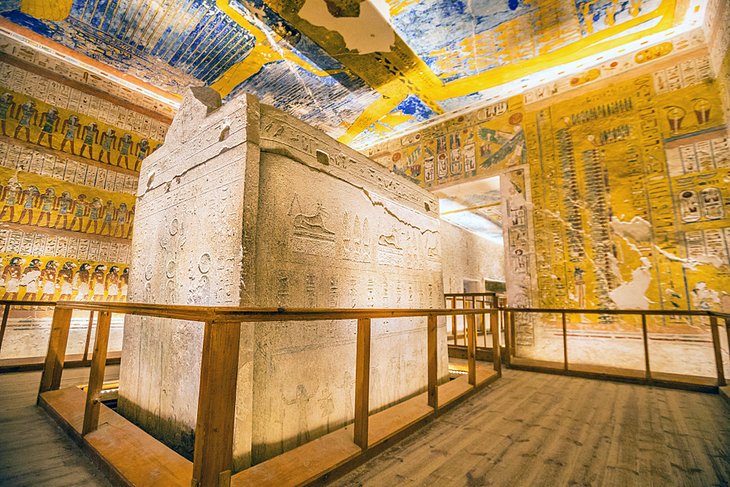

Hidden between the rocky escarpments of Luxor's west bank, the Valley of the Kings was the final resting place for the kings of the 18th, 19th, and 20th dynasties.
Covered in intricately detailed, vibrant wall-paintings, the tombs are normally every visitor's number-one stop on a West Bank visit.
Since it was believed that the dead, accompanied by the sun god (or perhaps having become one with the sun god) sailed through the underworld at night in a boat, the walls of the tombs were adorned with texts and scenes depicting this voyage and giving the dead instruction on its course.
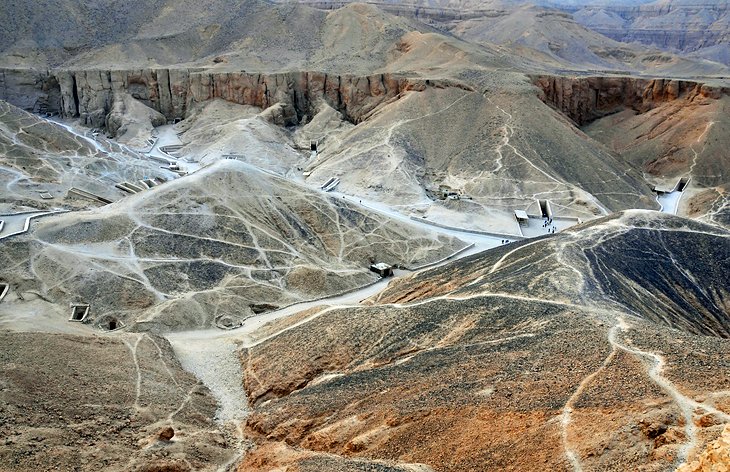

Within the valley are 63 tombs, which are a roll-call of famous names of Egyptian history, including the famous boy-king Tutankhamun.
The tombs are open on a rotation system to preserve the paintings as much as possible from the damage caused by humidity. Head here first thing in the morning (the site opens at 6am) to see them completely without the crowds.
- Read More: Exploring The Valley of the Kings: A Visitor's Guide
3. Hot Air Balloon Ride over Luxor at Sunrise
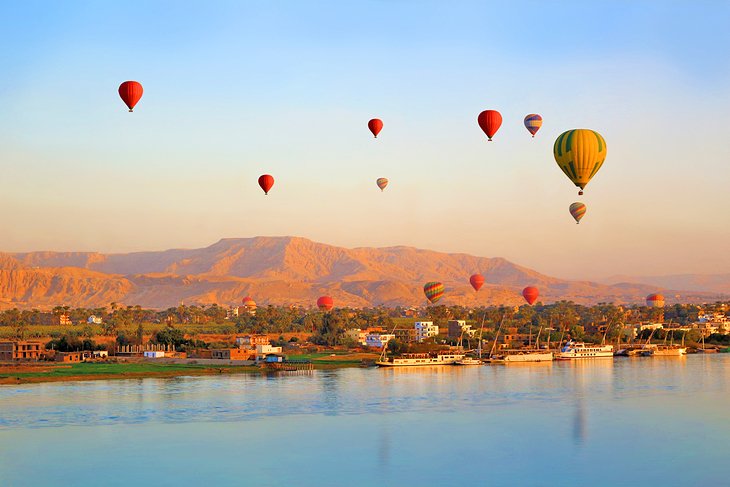

Early birds willing to roll out of bed while it's still dark are rewarded with a bird's-eye view of the West Bank on a dawn hot-air balloon ride.
Balloon rides here take off just after sunrise and float over the West Bank, with its green farming fields tucked between the barren escarpments, viewing the area's temples and tomb sites from high above.
Flight time is usually around 45 minutes, though expect the hot-air balloon tour experience to take around three hours from pickup at your hotel to being dropped back there.
There are a variety of operators in town. Balloon group tours generally use larger baskets taking around 24 passengers plus pilot.
4. Luxor Temple
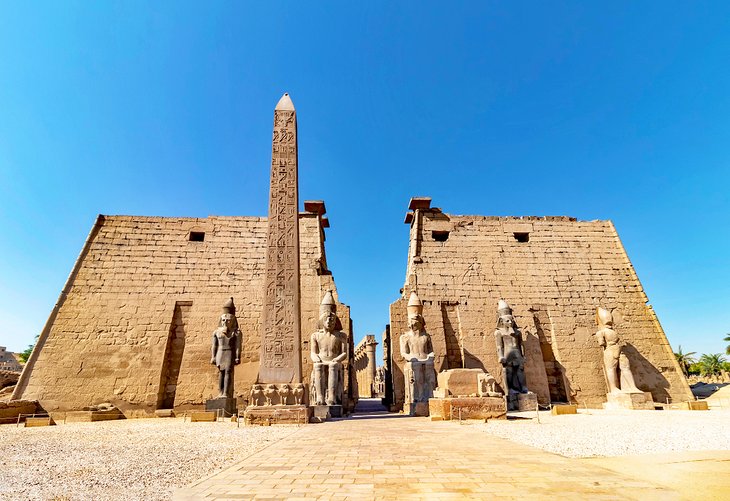

Presiding over the modern downtown district, Luxor Temple is an ode to the changing face of Egypt through the centuries.
Built first by Amenophis III (on the site of an earlier sandstone temple), it was known as "the southern harem of Amun" and was dedicated to Amun, his consort Mut, and their son the moon god Khons.
Like all Egyptian temples, it comprises the chapels of the deities, with their vestibules and subsidiary chambers; a large Hypostyle Hall; and an open Peristyle Court, which was approached from the north by a great colonnade.
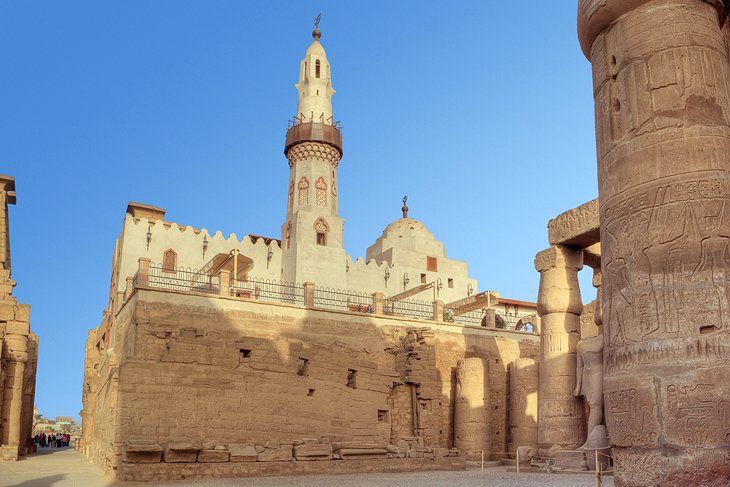

The temple was added to and changed by a parade of pharaohs, including Amenophis IV (who obliterated all references to the god Amun within the temple and added the Sanctuary of the god Aten), Tutankhamun (who had the walls of the colonnade embellished with reliefs and in turn destroyed the Temple of the Aten), Seti I (who restored the reliefs of Amun), and Ramses II (who extended the temple significantly, adding a new colonnaded court at the north end).
During the Christian era, the temple underwent a transformation into a church, while in the Islamic period, the Mosque of Abu el-Haggag, dedicated to a revered holy man, was built inside the complex grounds.
Address: Luxor Corniche, East Bank
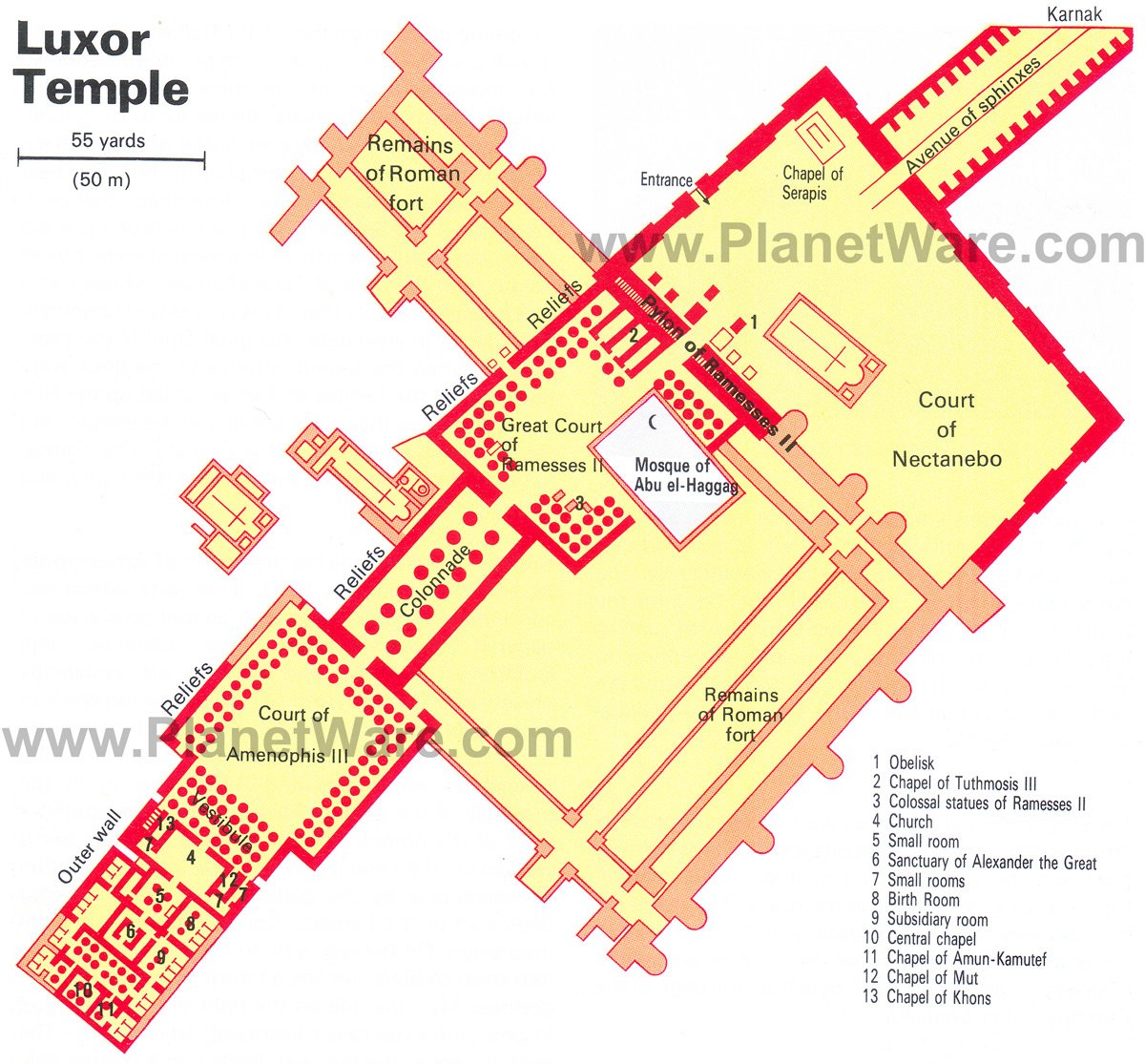
5. Temple of Deir al-Bahri (Queen Hatshepsut's Temple)
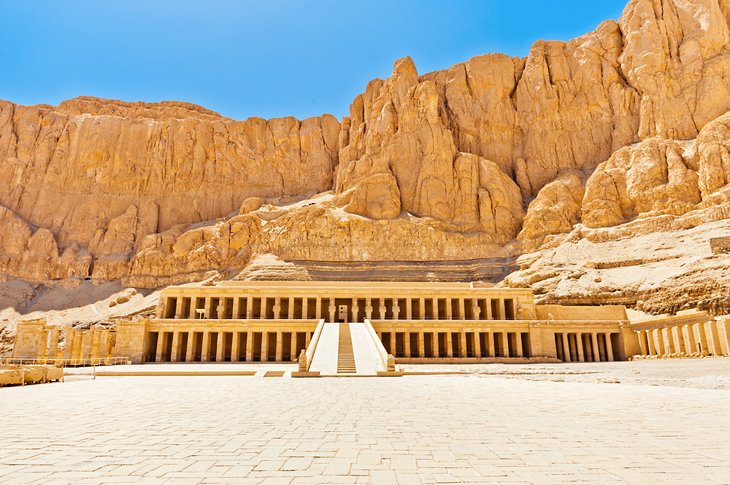

The Temple of Deir el-Bahri is magnificently situated on the West Bank, at the foot of the sheer cliffs fringing the desert hills, the light-colored, almost white, sandstone of the temple standing out prominently against the golden yellow to light brown rocks behind.
The temple complex is laid out on three terraces rising from the plain, linked by ramps, which divide it into a northern and a southern half. Along the west side of each terrace is a raised colonnade.
The terraces were hewn out of the eastern slopes of the hills, with retaining walls of the finest sandstone along the sides and to the rear. The temple itself was also partly hewn from the rock.
Inside, the complex is richly adorned with statues, reliefs, and inscriptions. Note how Queen Hatshepsut had herself represented with the attributes of a male pharaoh (beard and short apron) to demonstrate that she possessed all the authority of a king.
6. Felucca Ride to Banana Island
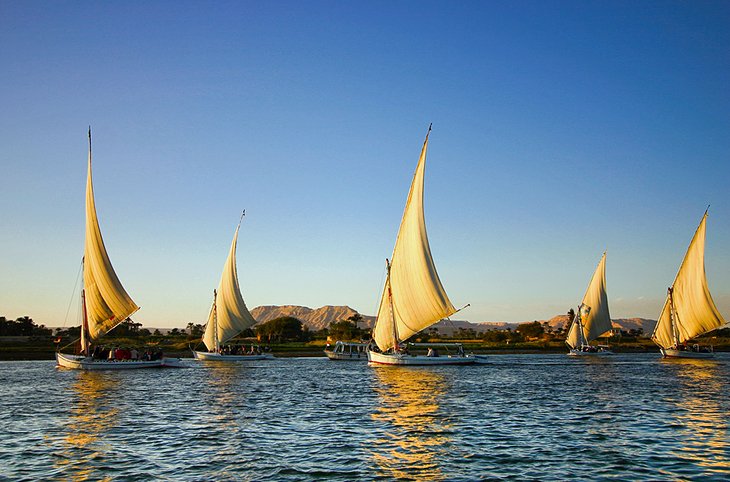

If you've had your fill of temples and tombs for the day, there is no better way to relax in Luxor than to take a felucca ride to Banana Island.
Sailing the five kilometers upriver from Luxor to this tiny palm-shaded island is the perfect chilled-out contrast to a dusty day exploring the Pharaonic treasures of the West and East Bank.
You'll have no problems chartering a felucca. Boat captains tout for customers all along the Nile-side Corniche Road in downtown Luxor. Boat rides are normally charged by the hour. Bank on a return Banana Island felucca taking around three hours.
Felucca rides are all about simply sitting back to watch the Nile-side views as the boat captain raises the sail and you slide up the river.
If you sail back just on sunset, you'll get to see the river at its most majestic.
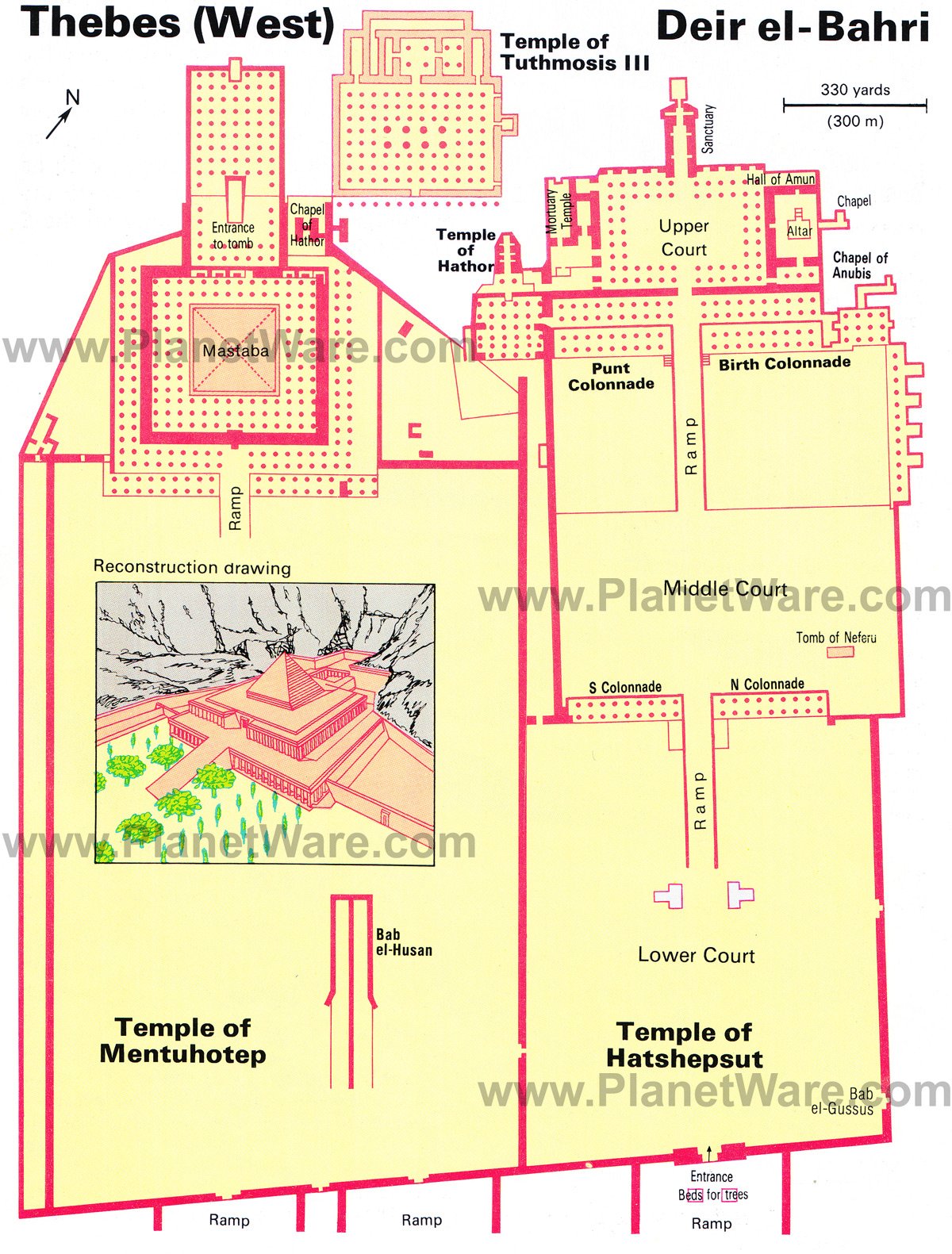
7. Medinet Habu
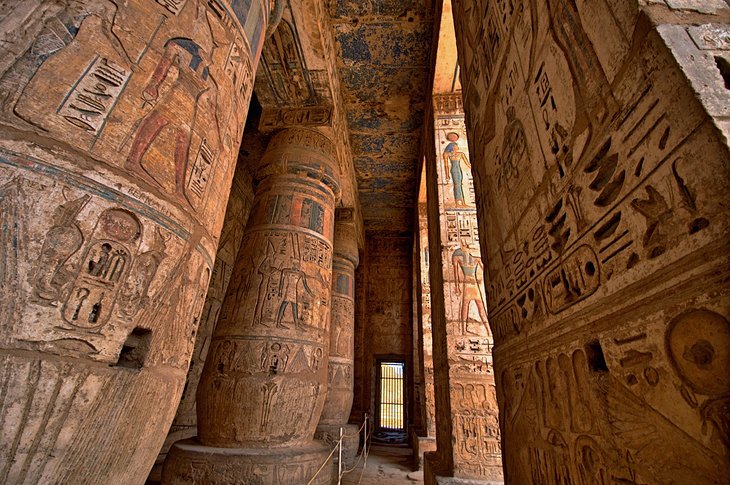

With the famous Valley of the Kings and Temple of Deir al-Bahri the main attractions, Medinet Habu often gets overlooked on a West Bank trip, but this is one of Egypt's most beautifully decorated temples and should be on everyone's West Bank hit list.
The complex consists of a small, older temple built during the 18th dynasty and enlarged in the Late Period, and the great Temple of Ramses III, associated with a royal palace, which was surrounded by a battlemented enclosure wall four meters high.
The main temple area was built exactly on the model of the Ramesseum and, like the Ramesseum, was dedicated to Amun. The reliefs here are some of the best you'll see on the West Bank.
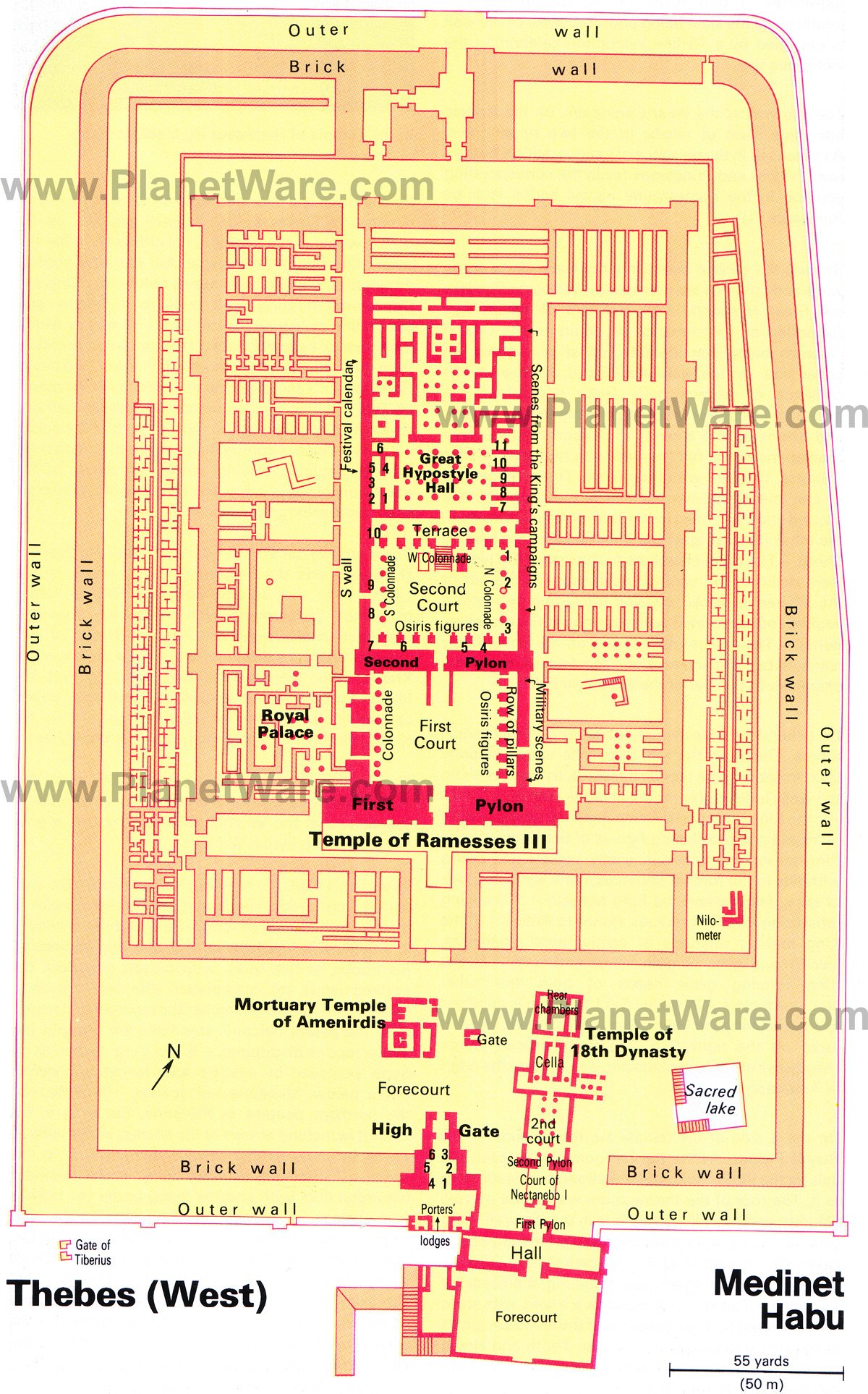
- High Gate
- Temple of Ramesses III
- South Tower
- 18th Dynasty Temple
- Sacred Lake
- Mortuary Temple of Amenirdis
- Forecourt
- 18th Dynasty Temple First Court
- 18th Dynasty Temple Second Court
- First Court
- Great Hypostyle Hall
- Royal Palace
- Second Court
- Second Pylon
8. Tombs of the Nobles
If you haven't had your fill of tombs in the Valley of the Kings then make a beeline for the Tombs of the Nobles, which may be less famous, but actually include much better preserved examples of tomb paintings.
This West Bank site contains around 400 tombs of various dignitaries, which date roughly from the 6th dynasty right up to the Ptolemaic era.
The tomb paintings here aren't so concerned with guiding the dead into the afterlife; instead, they showcase scenes from Egyptian daily life.
In particular, the Tomb of Sennofer, Tomb of Rekhmire, Tomb of Khonsu, Tomb of Benia, Tomb of Menna, and Tomb of Nakht are home to some of Egypt's most vivid and lively tomb paintings.
If you're short of time, opt to see the Tomb of Sennofer and Tomb of Rekhmire. Both have incredibly detailed paintings depicting scenes from the men's daily lives, work, and family life. Sennofer was an overseer during the reign of Amenhotep II, while Rekhmire was the pharaoh's vizier.
9. Colossi of Memnon
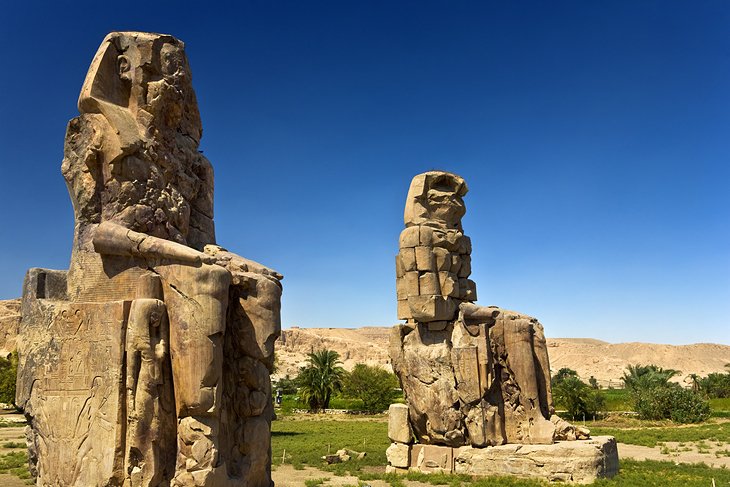

The Colossi of Memnon are the first monuments most travelers see on the West Bank. These giant statues sit beside the main road, that runs from the Luxor suburb of Al-Gezira on the west shore of the Nile bank, just before the main West Bank ticket office.
Carved out of hard yellowish-brown sandstone quarried in the hills above Edfu, they represent Amenophis III seated on a cube-shaped throne, and once stood guard at the entrance to the king's temple, of which only scanty traces are left.
In Roman Imperial times, they were taken for statues of Memnon, son of Eos and Tithonus, who was killed by Achilles during the Trojan War.
The South Colossus is better preserved than the one to the north. It stands 19.59-meters high and the base is partly buried under the sand. With the crown that it originally wore but has long since vanished, the total height must have been some 21 meters.
The North Colossus is the famous "musical statue," which brought flocks of visitors here during the Roman Imperial period.
Visitors observed that the statue emitted a musical note at sunrise and this gave rise to the myth that Memnon was greeting his mother, Eos, with this soft, plaintive note. The sound ceased to be heard after Emperor Septimus Severus had the upper part of the statue restored.
If you walk behind the statues, you can see the vast site (currently being excavated by archaeologists) where Amenophis III's temple once sat.
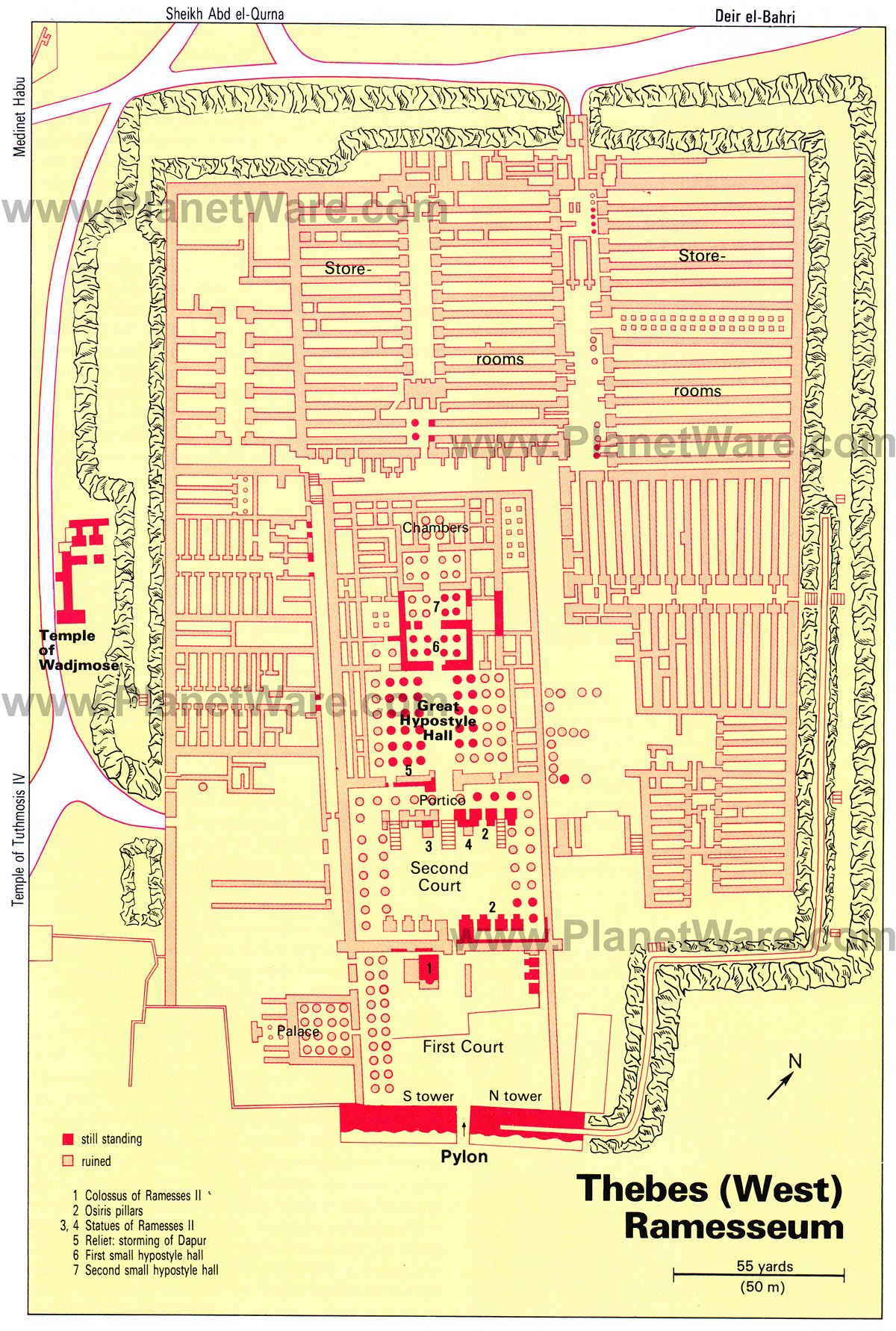
10. Ramesseum
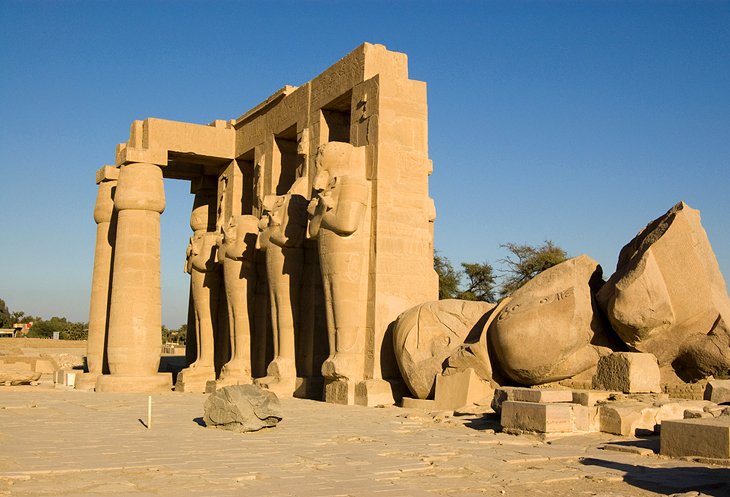

The great mortuary temple built by Ramses II and dedicated to Amun, lies on the edge of the cultivated land, some one-and-a-half kilometers south of Deir el-Bahri on the West Bank.
Although only about half of the original structure survives, it is still a highly impressive monument.
During the Roman Imperial period, it was known as the Tomb of Ozymandias, mentioned by the historian Diodorus (1st century BC) and was later immortalized by the English poet Shelley in his poem Ozymandias.
The north tower and south tower are inscribed with reliefs of Ramses II's battle with the Hittites, similar to the reliefs of Abu Simbel.
On the South Tower, the whole of the left hand half of the wall is taken up by the Battle of Qadesh. Scenes here portray Ramses in his chariot dashing against the Hittites, who are killed by his arrows or flee in wild confusion and fall into the River Orontes, while to the right, you can make out the Hittite Prince and the enemy fleeing into their fortress.
Inside the First Court are the remains of a colossal figure of the king, which is estimated to have originally had a total height of 17.5 meters and to have weighed more than 1,000 tons.
11. Valley of the Queens
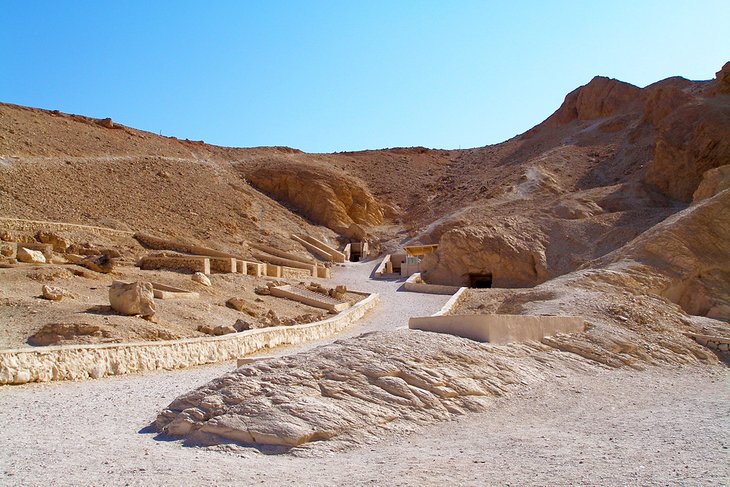

The tombs in the Valley of the Queens, on the West Bank, mostly belong to the 19th and 20th dynasties. A total of almost 80 tombs are now known, most of them excavated by an Italian expedition led by E. Schiaparelli between 1903 and 1905.
Many of the tombs are unfinished and without decoration, resembling mere caves in the rocks. There are few incised inscriptions or reliefs, with much of the decoration consisting of paintings on stucco.
Only four tombs are open for public viewing, but one of the group is the famed Tomb of Queen Nefertari, only reopened in 2016, making a trip here well worth it.
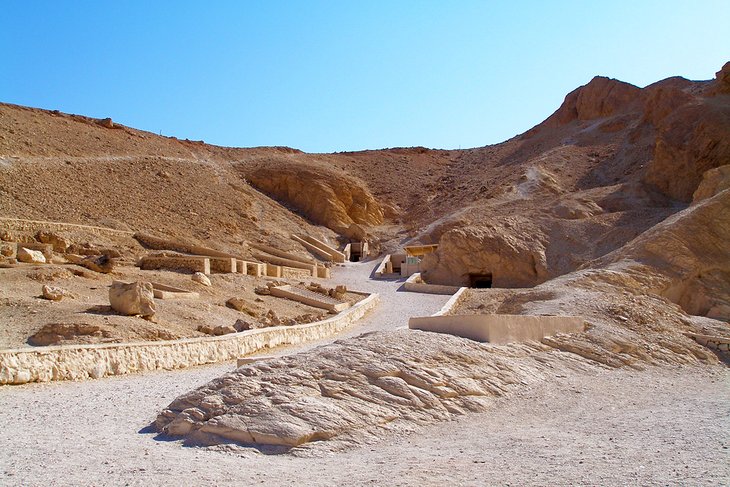

The Tomb of Queen Nefertari, Wife to Ramses II, is regarded as the finest of the West Bank's glut of tombs. The walls and ceilings of the chambers here are covered with dazzling, highly detailed and richly colored scenes, which celebrate Nefertari's legendary beauty.
Of the three other tombs that can be seen here, the Tomb of Prince Amen-her-khopshef is the best, as the wall paintings of its chambers have well-preserved colors. A son of Ramses III, Amen-her-khopshef died while still a teenager.
If you have time, or simply just like tombs, the Tomb of Khaemwaset (another son of Ramses III) and the Tomb of Queen Titi both contain some interesting preserved scenes, though those in the Titi tomb are more faded than Khaemwaset. There is no consensus in the archaeology world over who Titi's husband was.
12. Luxor Museum

One of Egypt's best museums, Luxor Museum holds a beautifully exhibited collection from the local area, which tells the story of ancient Thebes, from the Old Kingdom right up to the Islamic Period.
The museum's prize possessions are the two Royal Mummies of Ahmose I and what is believed to be Ramses I in two rooms on the ground floor, which are worth a visit here alone.
The upper floor has a dazzling display of amulets, silver bowls, grave and tomb furnishings, and votive tablets running across the middle of the floor space.
While here, check out the reliefs on the re-erected Wall of Akhenaten. The 283 sandstone blocks are covered with painted reliefs and originally belonged to Akhenaten's Temple of the Sun at Karnak.
Address: Luxor Corniche, East Bank
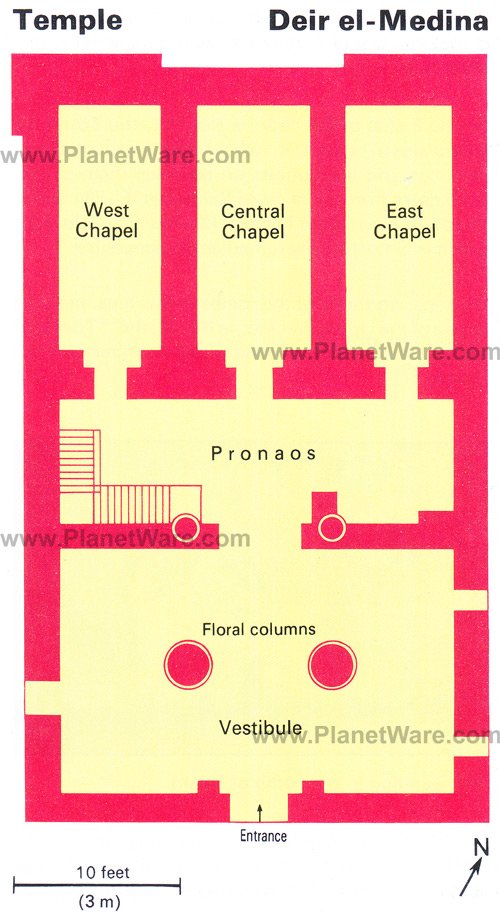
13. Deir el-Medina
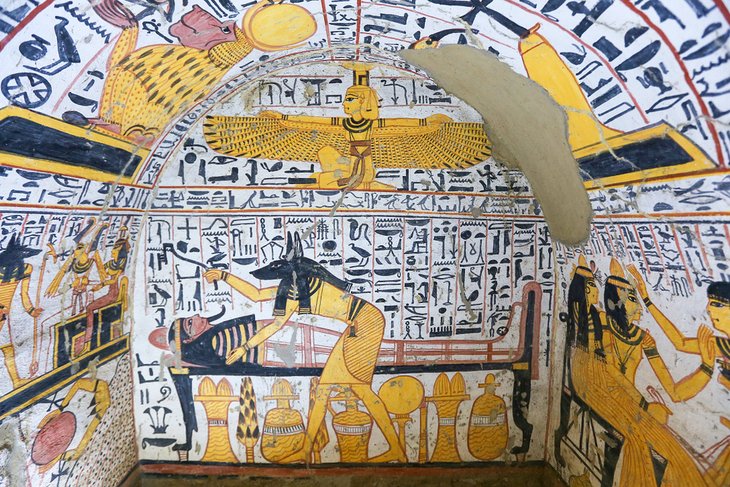

Deir el-Medina, on Luxor's West Bank, is home to a small temple, the remnants of a workers' village (where the artisans of the royal tombs lived) and the tombs of the workers themselves.
It's well worth a visit for the wall paintings adorning the tombs, which differ in style from those that decorate the pharaoh tombs and are a vibrant depiction of daily Egyptian life.
Don't miss the Tomb of Sennedjem, who was a 19th-dynasty artist. It has a vaulted tomb chamber and reliefs and paintings on religious themes, including a fine representation of a funeral banquet. The contents of the tomb – discovered in 1886 – are now on display in Cairo's Egyptian Museum.
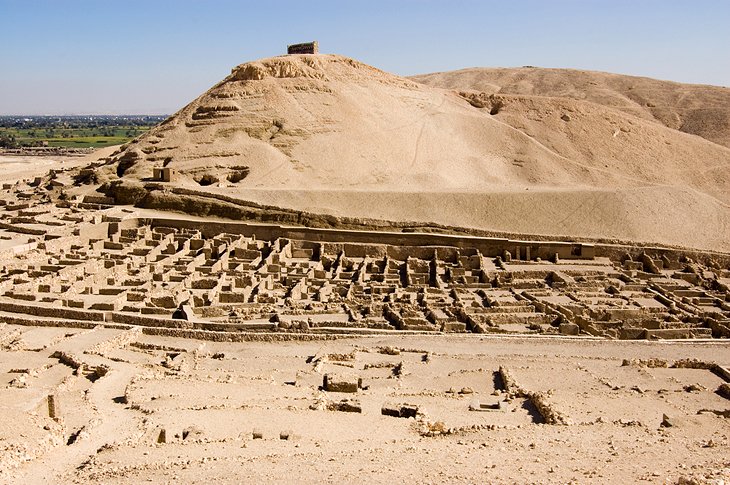

After viewing the tombs, walk through the ruins of the workmen's village up to Deir el-Medina's temple, which sits on the escarpment behind. The small temple is a much younger addition to this site, dating from the Ptolemaic era and dedicated to the god Hathor.
Location: West Bank
14. Mortuary Temple of Seti I

The Mortuary Temple of Seti I, on Luxor's West Bank, is dedicated to Amun and to the cult of the king's father Ramses I.
Left unfinished by Seti I, it was adorned by Ramses II with reliefs and inscriptions, which vie in quality with the contemporary work at Abydos.
The temple was originally 158 meters long, but all that now remains is the sanctuary, with its various halls and chambers and some scanty fragments of the courts and pylons.
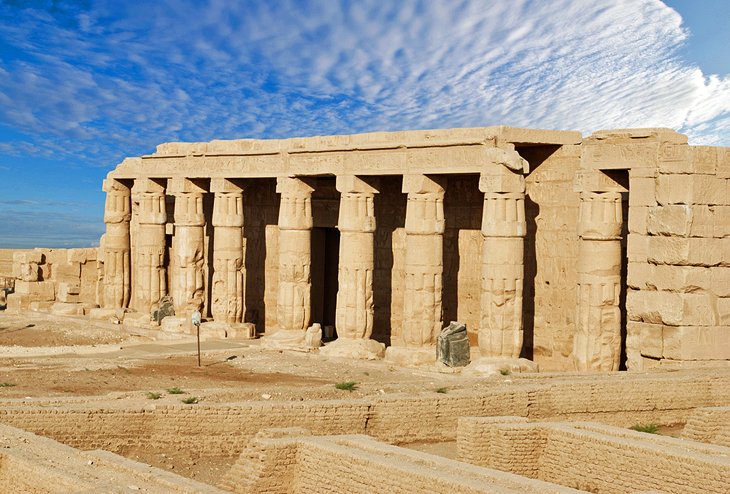

For those travelers interested in ancient Egyptian decorative work, the temple's Hypostyle Hall contains some excellent examples of reliefs.
On the roof slabs over the central aisle are the winged solar disc; flying vultures; and the names of Seti I, enclosed by snakes and flanked by two rows of hieroglyphics.
The low reliefs on the walls depict Seti I and Ramses II making offerings to various gods, including, on the right, Hathor of Dendera who is suckling Seti.
15. Tomb of Tutankhamun Replica & Carter's House
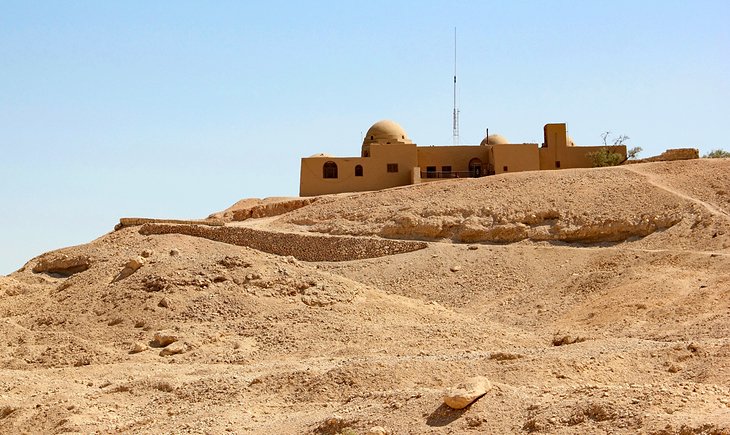

This modest mud-brick house is where Carter set up home during the long search for Tutankhamun's tomb. In the garden here, you can also visit an exact replica of the Tomb of Tutankhamun from the Valley of the Kings.
The tomb replica's burial chamber is an exact copy of the original down to the finest detail, including dust. It was created by the Factum Foundation for Digital Conservation in collaboration with Egypt's Ministry of Antiquities as an experiment in contemporary preservation.
Millions of tourists come to Egypt each year specifically to see this country's Pharaonic tombs and temples but at the same time, that footfall into the sensitive atmosphere of the tombs is heavily degrading them. Come here to be wowed at just how perfect the replica is, and consider how replicas like this could be used to help conserve original sites in the future. You can't spot the difference.
Carter's House itself has been restored, with the rooms laid out as they would have been while he lived here, and the walls display interesting black-and-white photographs documenting his work.
The site is on the main West Bank road, just past the turnoff that leads to the Mortuary Temple of Seti I.
16. Mummification Museum
This small but fascinating museum, in downtown Luxor, explains the processes behind the ancient Egyptian practice of mummification in a series of well set out and informative displays.
The exhibits include actual mummies (both human and animal) and the tools (including the spatulas used to scrape the dead person's brains out) used in the mummification process.
It's probably not the best museum for anyone particularly squeamish, but the clear information panels and well-thought-out exhibits are a must for anyone looking to find out more about the burial practices of the pharaohs.
In particular check out the mummy of Maserharti, a high priest of Amun in the 21st dynasty, which is extremely well-preserved.
Address: Luxor Corniche, East Bank
Where to Stay in Luxor for Sightseeing
The East Bank has the vast amount of accommodation, though staying on the West Bank is increasingly popular, particularly if you want to hit the tombs and temples early.
Luxury Hotels:
- The Sofitel Winter Palace is Luxor's most famous hotel and its oldest. It has lush gardens and pools and one of the top restaurants in town, as well as bags of historic ambience.
- The Hilton Luxor Resort & Spa has a wonderful spa, multiple restaurants, and an infinity pool overlooking the Nile.
Mid-Range Hotels:
- The Jolie Ville Hotel & Spa - Kings Island is based on a private island on the Nile. There's plenty of resort features, with gorgeous grounds, three outdoor pools, tennis courts, and a fitness center.
- Popular with tour groups, the Steigenberger Nile Palace Luxor has good-value rates, Nile River views, beautiful pools, and nightly entertainment.
Budget Hotels:
- The Nefertiti Hotel is one of the most popular budget choices on the East Bank thanks to its friendly staff, roof terrace, great restaurant, and squeaky-clean rooms right in the center of town.
- On the West Bank, El Masala Hotel is near the ferry terminal in Al-Gezira, close to town as well as the West Bank sites. There's a pool and restaurant, and most rooms come with balconies that overlook the Nile.

Nice post.
ReplyDelete